Hurray! Yesterday, the Dalberg report (click here for PDF) was released to describe the impact of the Internet in some African countries, including Ghana. This is the type of report that a blogger needs when asked “…but really, can the Internet have an impact in Ghana?”
The report openly target policy makers in Ghana ( Kenya, Senegal and Nigeria) and focuses on “potential” and findings such as “more than 80% of SME owners expect that the Internet will help them grow their business, and 70% of those expect to hire new employees as a result.”(p.7) It also comprehensively compares the countries with a model that takes into consideration “core” (from infrastructure to business environment and school enrolment rates) and “conditions for usage” (from percentage of households with electricity to mobile and broadband subscriptions to uploads of video!). Here we can see that over the past six years, Ghana significantly improved the “core”, but not the “conditions for usage”. They recommend government to play a role.
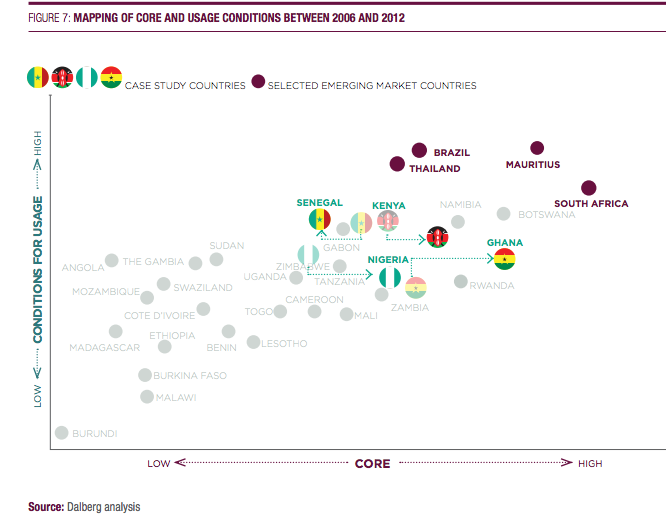
My understanding of this, but detailed data could tell if I am right, is that although we have the core or the basics in place, for some reason the conditions for usage and hence reach does not follow. It is still expensive to access Internet in Ghana and despite competition bordering on overcrowding, data is not becoming cheaper.
Here are 5 other findings from the report I thought were interesting and my corresponding comments:
1. Ghana Rocks Social Media
“[Ghana] shows comparatively high engagement in social media, content generation on Wikipedia and video sharing. These build atop its leading position in mobile broadband penetration on the continent, relieving barriers to higher bandwidth interaction. Despite this strong performance, our analysis suggests that Ghana now needs to focus its attention on improving the level of attractiveness of Internet services” (p.11)
We often complain about access, but comparatively (with other African developing countries), we are doing fine. Also, I am happy to read that content creation, as recently discussed at BlogCamp13 is relatively good. Although mobile broadband is fine, it is still expensive especially for data intensive operations such as uploading video.
2. The promise of social media for government and citizens
“Social media and social networking is proving to be a catalyst in driving Internet access and impact….Social networks can create stronger links between government, educators, service providers, businesses and citizens. Users are already engaging on topics including music, dating and sport, but these networks are also quickly expanding to include education, health information and governance, and will undoubtedly influence how users engage in more sophisticated Internet
use over time.” (p.3)
This point cannot be overstated and it is A GOLDEN OPPORTUNITY for Ghana and other countries in Africa with traditionally not very cosy relations between citizen and state.
3. Wider Access Completely Changes the Game
“Internet penetration also opens up entirely new business models for both companies with technical expertise as well as entrepreneurs. In Nigeria, for example, it has created opportunities for software designers developing gaming applications and mobile traffic applications, such as Maliyo Games, Gidi Traffic and Road Peer. It has also created opportunities for traditional and new media companies via advertising revenues, bringing in over 5M Naira a month for bloggers such as BellaNaija and Linda Ikeja, discussion forums like Nairaland, and newspapers such as Vanguard. Vanguard’s print business was unprofitable on its own, but its online portal ranks as the twelfth most popular site in Nigeria, and generates enough advertising revenue to make the entire operation viable.” (p. 17)
In Nigeria, bloggers make a living on what they do. So far in Ghana, there are just a handful bloggers who can , Ameyaw Debrah is the one that springs to mind, and maybe a few others who consult alongside their websites. Still, there seems to be no profitable way of advertising online in Ghana (although I believe a MEST start-up Adsbrook is working on it) . Is it a volume issue? What if Internet reached not only the population it reaches today (18% or 4,1%), but twice as many households?
4. Access is key
What is this report about? I think this word count exercise will tell you in a blink! The word “access” was used 234 times, “mobile” 134 times, “growth” 112 times, “broadband” 42 times, “open data” 24 times, “blog” just 7 times, “political” only 3.
5. What about Political Impact?
Following the exercise above…If to look broadly at “impact” there were some important political initiatives such as Enough is Enough Nigeria and GhanaDecides that were not mentioned. I suspect that is because these were not initiatives that made economic impact (not directly at least), but rather focused on governance. But as we all know, they are interlinked! A chapter on political impacts of Internet (and political potential) including transparency, accountability and governance would have added that which, according to the Dalberg report:
“available studies typically lack detailed analyses of the social and political value of the Internet, especially across Sub-Saharan Africa.”
That is, if you want to call a report “impacts of the Internet”, include all major impacts. Else, “economic impacts” might be a better title.
All in all, this is an amazing report that I will be referring to for a long time. I only wish details of the computation leading up to the table posted above would be shared, maybe on the companion website for the report? Thanks to Google Africa for sponsoring (commisioning?) this useful report.
Other places for Internet information concerning Ghana are: Afrinnovator’s Ghana Page, History of Internet in Ghana from GhanaWeb (not well written, but an interesting reminder) and another historic reminder from Colunmbia University (from 2005?) Internet World Stats (last figures from 2009), Internet Governance Forum Ghana and Research ICT Africa.
